How to fix website error codes
Attempting to load a website and being greeted with an error code is very annoying. This is especially true for website owners as sites experiencing these issues can lose traffic, see reduced search visibility, and will provide a poor user experience.
In this guide learn more about HTTP errors, what causes them and potential resolutions for each one. This will help you on your way to resolving those issues efficiently and with minimal downtime.
Error Code 400 – Bad Request
This error indicates that the server cannot process a request due to client-side issues. It often stems from syntax errors, invalid formatting, or oversized payloads.
Common Causes
- Corrupted browser cache or cookies
- Malformed URL or syntax errors
- Uploading files that exceed server size limits
- Incompatible or mismatched request headers
Potential fixes
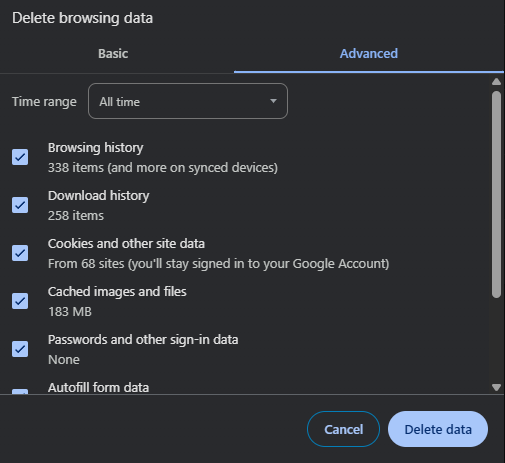
- Clear your browser cache and cookies to remove stored conflicts.
Below is an example of clearing the cache and cookies in Chrome browser.
- Review the URL for any typos or formatting mistakes.
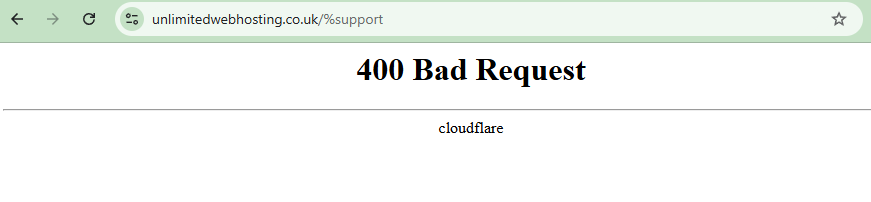
Sometimes this is more obvious as the 400 error will be accompanied by Invalid URL. In this case you can see the issue might be in the URL itself.
- Reduce the size of uploaded files to meet server limitations.
- Check that headers in your requests align with what the server expects.
Fixing Error Code 401 – “Unauthorised”
A 401 error means the request lacks valid authentication credentials. The server refuses access until proper login details are provided.
Common Causes
- Missing or incorrect login credentials
- Expired session tokens or cookies
- Insufficient user permissions
- Misconfigured server authentication rules
Potential fixes
- Confirm your username and password are correct.
- Log out of your session and sign back in to refresh authentication.
- Clear your browser cookies, then restart the browser. If you’re using chrome follow on from the 400 bad request guide.
- Double-check API keys or tokens if accessing via a third-party tool.
- Contact your site administrator if you’re unsure about access rights.
Fixing Error Code 403 – “Forbidden”
Even with correct login credentials, a 403 error means access is denied due to permissions or server rules.
Common Causes
- User lacks sufficient access privileges
- IP address blocked by firewall or ruleset
- Incorrect file or directory permissions on the server
- Server-level security tools denying access
Potential fixes
- Ensure your user role has permission to access the resource.
- Ask the administrator to review your access level.
- On the server, verify permissions for relevant files or directories.
- Temporarily disable security plugins or whitelist your IP if applicable. You can do this from the WP Toolkit available in cPanel.
Fixing Error Code 404 – “Not Found”
A 404 error occurs when the requested resource cannot be located on the server. While common, frequent 404s can negatively impact SEO and usability.
Common Causes
- Mistyped URL or outdated link
- Deleted or moved content without redirection
- Server misconfiguration preventing proper routing
- DNS resolution issues
Potential fixes
- Check the URL for spelling and path accuracy.
- Reload the page or test it in a different browser.
- Locate missing files or update internal links to point to valid pages.
- Implement 301 redirects for permanently moved content.
- Flush the DNS cache or try a different network to rule out local issues.
